Online Charging System|OCS Billing|Real Time Charging System
Get the tried and tested Online Charging System to implement prepaid mobile services. OCS is also referred to as Real Time Charging or Prepaid Billing system in the Telecom Billing circles. Typically, the prepaid mobile services allow for calling and mobile data usage on a SIM card. In prepaid services, the customer pays an amount equivalent to that of the plan being offered, before starting to use the services. The service cannot become functional unless there has been a prepaid payment (or a top up). The OCS system is a required system for implementing and offering prepaid services.
What is an Online Charging System?
The Online Charging System OCS is a system that allows telecommunication companies to charge customers instantly based on their service usage. OCS does instant calculations and takes decision according to customer’s available account balance.
What does an Online Charging System do?
The Online Charging System interfaces with a network component of a Telecom Operator. This network component is a piece of equipment (hardware) and some software. In many cases, the Telecom Operators use the Universal Gateway (or a UGW offered by various providers). The UGW captures the request for usage made by the subscribers, and passes it to the Online Charging System.
Typically, OCS then validates the following 3 things:
-
-
- the subscriber’s available balance,
- usage quota made available on the plan and
- the recharge expiry date.
-
If OCS finds that all 3 checks are passing, it responds back to the UGW (or a similar network component) confirming that the usage of the particular service can continue as there is sufficient balance or quota present for that subscriber.
The subscriber must start his or her prepaid services by buying the subscription with the Telecom operator. This is done by purchasing a new plan, the SIM and making a payment of the fees involved as a top up transaction. Many Telecom Operators also support the concept of a Wallet.
What is a Wallet and a top-up transaction?
The Wallet is nothing but a virtual account maintained by the subscriber with the Telecom Operator. The top up transaction increases the Wallet balance, whereas the allocation of a prepaid plan by the Telecom Operator to the subscriber will reduce the Wallet balance (marking that balance in use). An automatic renewal of the plan can take place at the end of the cycle (typically monthly) by deducting the available balance from the Wallet. If the balance in the Wallet is not sufficient, then the auto renewal will fail and the service will be disconnected. A new recharge will ensure that the service can start back again.
How does the Online Charging System (OCS) function?
The Online Charging System or OCS is implemented by using a software (listener component) which listens to specific requests originating from either a diameter client or a radius client. Each diameter or radius message emanating from the client (or the UGW) is picked up by the Diameter or a Radius Server implemented within the OCS. This post is written considering Radius protocol rather than Diameter, however similar concepts apply with Diameter with some differences.
The radius message could be of 4 types:
-
-
- An Access Request,
- An Accounting Start Request,
- An Accounting Intermediate Update Request, and
- An Accounting Close Request
-
- Access Request – The UGW system creates a user session and requests for Authentication to the triple A (AAA) system in case of Diameter implementation. In case of Radius implementation, the OCS platform can provide the authentication response by verifying the authenticity of the access request.
- Accounting Start Request – When the access request has been accepted by the radius server (or the OCS), then the UGW gets a confirmation that the usage can now start for the particular subscriber and service. When the usage starts, the UGW sends an Accounting Start request to the Radius server (or OCS) indicating that the usage session has been started.The Radius server or OCS receives the Accounting Start Request and responds to it in affirmative in there is sufficient quota for the subscriber to continue with the service. There might be usage consumption minutes or bytes on the Account Start Request or not, it depends on the usage.
- Accounting Intermediate Update Request – Once the Accounting Start Request is responded in the affirmative by the OCS, the next requests will be that of intermediate update. The session update requests are sent periodically by the UGW to the OCS as long as the user session (a call or a data usage session) is on. The update request will be processed by updating the usage quota or the subscriber balance.The update requests are periodical and recurring during the course of the call or data session. For example, they may recur every minute or every 5 minutes or when the usage exceeds certain limit. In case of data session, the interim radius message could occur every 5 mins or after utilising 50 MB of data, whichever is earlier.
- Accounting Close Request – An Accounting Close Request indicates that the subscriber has closed the usage session and the OCS marks session as ‘invalidated’. Then the next user session will be expected to be with another session id.
Which type of usages can be processed and charged by an OCS system?
An OCS system can charge usage for varying types of Telecom services such as the SMS, MMS, Calls, Mobile Data, Video, API calls etc. These usage types are either event based or session based. For example, the SMS and MMS don’t involve an active user session, instead they are more like events. The Calls or Mobile Data Usage on the other hand involve an active user session that can last from a few seconds to some hours.
Depending on the type of usage that needs processing, there are 2 types of implementations possible for an Online Charging System, mainly:
-
-
- Session Based Charging
- Event Based Charging
-
Session Based Charging
In Session Based Charging, the network hardware component (like UGW or Universal Gateway) creates a user session and keeps sending the usage in the Radius or Diameter messages. Each session starts with an authentication message followed by periodic usage update messages that carry the actual usage in minutes for calls and in bytes for data.
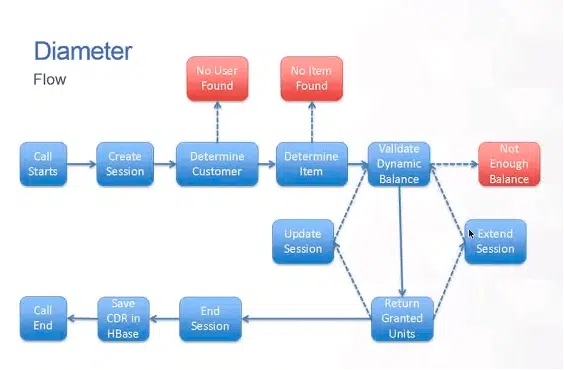
As shown in the above diagram, in the session based charging, the customer account balance is validated at realtime and the user session (either for call or data usage) continues if there is sufficient balance. The new usage is continuously received at periodic intervals as RADIUS messages and the balance checked at realtime. When the user session ends, the Call Data Record (CDR) or Usage Detail Record (UDR) is saved to the database in the OCS platform.
Event Based Charging
In the Event Based Charging, the Call Data Record (CDR) event is sent to the billing system after the event has occurred. In this case, the first message from RADIUS will be processed to check if sufficient balance exists on the customer account. The response of this message could also provide information about total units that can be consumed by the user. The final charging event could occur from the network component after the event.
The EarnBill’s OCS platform supports both session based and event based charging. The system can be easily customised to meet unique needs of Telecom companies.
EarnBill Support Diameter Protocol or Radius Protocol with OCS Platform
EarnBill supports both the Diameter protocol as well as the Radius protocol while accepting messages emanating from a triple A (AAA) system (which stands for Authentication, Authorization and Accounting). EarnBill’s OCS platform also has the ability to replace the triple A system (AAA) by supporting the authentication and authorization, and then processing the message with the billing system to validate the usage quota.
There is a good amount of flexibility while integrating EarnBill’s OCS system into your application ecosystem. Whether the OCS system will play the role of AAA + OCS or just OCS system really depends on your existing or planned application + network infrastructure.
